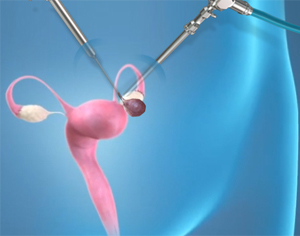
What is Laparoscopic Ovarian Cystectomy?
Laparoscopic ovarian cystectomy is a surgical procedure to remove a cyst or cysts from one or both of the ovaries laparoscopically.
An ovarian cyst is a fluid-filled sac or a muscular pouch that grows on an ovary. The ovaries are two small, bean-shaped organs that are part of the female reproductive system located on each side of the uterus that produces eggs and female sex hormones, estrogen, and progesterone.
Laparoscopy, also known as keyhole surgery, is a minimally invasive surgical technique where a laparoscope - a flexible fibre-optic lighted instrument attached with a camera - is introduced into the abdomen or pelvis through a few small keyhole incisions along with tiny specialized instruments to visualize, diagnose, and repair abnormalities of the structures.
Symptoms of Ovarian Cysts
Some of the common symptoms of ovarian cysts include:
- Pain in the abdomen or pelvis
- Pain during intercourse
- Abdominal swelling or bloating
- Irregular, heavy, or lighter periods
- Urinary frequency
- Painful bowel movements
- Breast tenderness
- Nausea and vomiting
Indications for Laparoscopic Ovarian Cystectomy
An ovarian cyst is indicated to be removed if it is:
- Causing pain symptoms
- Suspected of being cancerous
- Larger than 6 cm in diameter
- Solid rather than spongy
Diagnosis of Ovarian Cysts
The diagnostic process for identification of ovarian cysts may involve:
- A routine pelvic examination to detect the presence of an ovarian cyst.
- An ultrasound exam to confirm the presence of an ovarian cyst and determine the shape, location, size, and composition of the cyst.
- A blood test to check the levels of certain hormones, such as estrogen, progesterone, luteinizing hormone (LH), and follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH).
- A CA-125 blood test to find out if the cyst is cancerous.
- A pregnancy test to rule out pregnancy.
- Other imaging tests such as CT scan, MRI scan, and Doppler flow studies can also help detect ovarian cysts.
Preparation for Surgery
Prior to the procedure, your doctor may check your preparedness for surgery by doing the following:
- A thorough physical exam
- Review of medications and supplements
- Blood tests
- Urine tests
- Imaging tests, such as CT scan, MRI scan, and ultrasound
Your doctor may also advise to:
- Stop taking certain medications or supplements if necessary
- Not to eat or drink anything at least 8 hours prior to surgery
- Arrange for a mode of transport to and from the hospital
- Arrange for help to assist you at home during recovery
- Refrain from smoking and abusing alcohol as it may complicate the recovery process
Procedure for Laparoscopic Ovarian Cystectomy
Cystectomy is a surgical procedure during which the ovarian cyst is removed either with laparoscopy or open surgery. However, laparoscopy is the preferred choice of most surgeons due to its advantages over open surgery.
Laparoscopic ovarian cystectomy will involve the following steps:
- General anaesthesia is administered to keep you asleep throughout the procedure.
- The surgical site is cleaned and a few small keyhole incisions are made below your navel.
- A laparoscope is inserted through one of the incisions.
- Carbon dioxide gas is pumped into the abdomen for better visualization of the organs and other structures through the laparoscope.
- Small miniature instruments are inserted through the other incisions to remove the cyst.
- Your surgeon identifies the cyst through the scope and removes it with the instruments.
- After the cyst is removed, the scope and instruments are removed, and the incision area is closed with stitches or staples.
Postoperative Care and Instructions
Post-procedure care and instructions will include the following steps:
- You will be transferred to the recovery area where you will be asleep until the anaesthesia wears off. It is normal for you to feel soreness in the navel and abdomen area once you gain consciousness.
- You may observe some vaginal discharge or spotting.
- You may feel pain in the back and shoulders as a result of the gas placed in the abdomen during surgery.
- Your doctor will prescribe pain medications to relieve pain.
- You should refrain from strenuous activity or exercise for at least a week.
- Your doctor will provide you with instructions on incision site care, diet, driving, and bathing.
- Complete recovery usually takes about one to two weeks, and you should gradually increase your activity level with short walks and light activities.
- You can resume sexual activity when you are comfortable.
- Follow-up appointments will be scheduled to monitor your progress.
Risks and Complications of Laparoscopic Ovarian Cystectomy
Laparoscopic ovarian cystectomy is a relatively safe procedure; however, as with any surgery, you may notice some risks and complications, such as:
- Bleeding
- Infection
- Blood clots
- Damage to nearby organs
- Infertility
- Recurrence of cyst
- Need for removal of the ovary
- Anaesthetic complications
Benefits of Laparoscopic Ovarian Cystectomy
Some of the benefits of laparoscopic ovarian cystectomy include:
- Small surgical cuts
- Minimal pain and bleeding
- Shorter hospital stay
- Faster recovery time
- Reduced scarring
- Reduced risk of infection
- Minimal damage to surrounding tissues
What If I Experience Any Problems During Recovery?
You should call your doctor to seek medical care if you experience:
- Severe pain that does not get better with pain medicine
- Signs of infection, such as fever and chills
- Swelling, redness, bleeding, or discharge from the incision site
- Increased vaginal bleeding or discharge
- Nausea or vomiting
- Urinary difficulties
- Cough, chest pain, or shortness of breath
- Headaches, lightheadedness, muscle aches, or malaise
- New and unexplained symptoms






